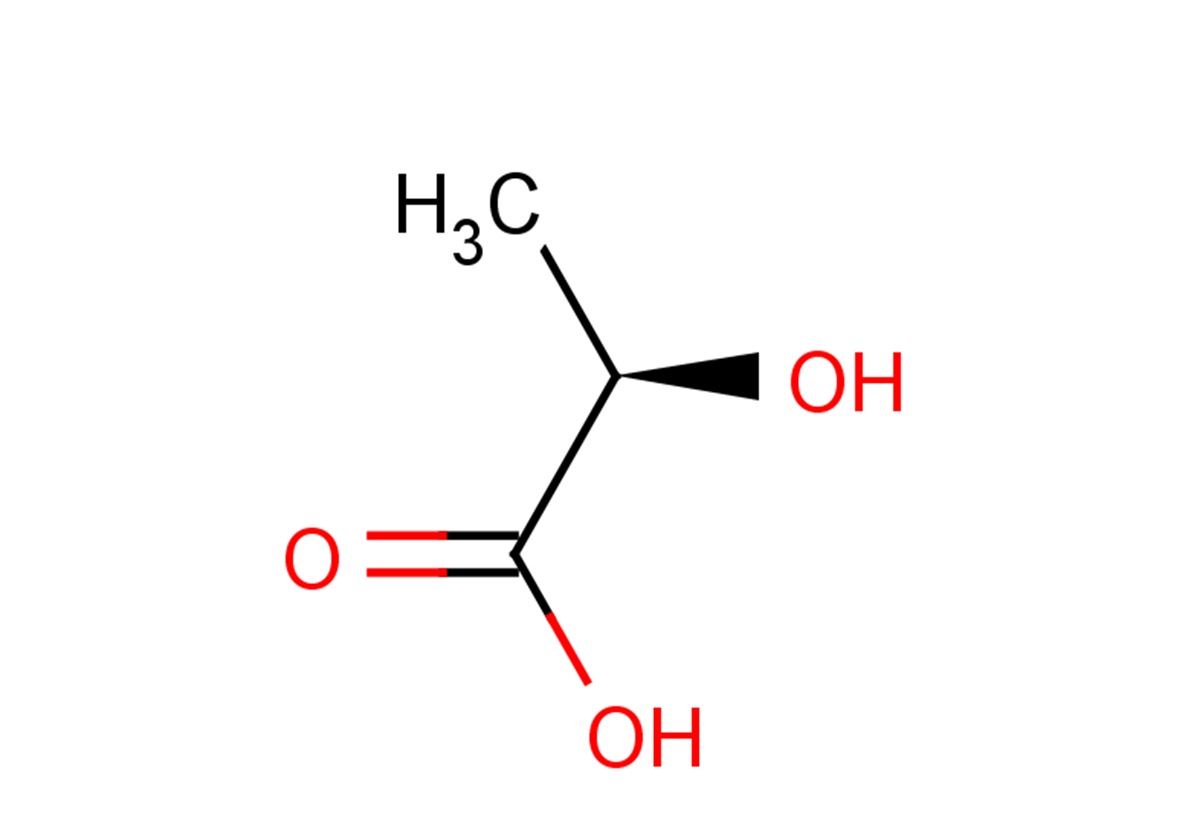
D-(-)-Lactic acid
CAS No. 10326-41-7
D-(-)-Lactic acid( (R)-2-Hydroxypropionic acid )
Catalog No. M23238 CAS No. 10326-41-7
D-(-)-Lactic acid is a normal intermediate in sugar fermentation (oxidation, metabolism).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 60 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 66 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameD-(-)-Lactic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionD-(-)-Lactic acid is a normal intermediate in sugar fermentation (oxidation, metabolism).
-
DescriptionD-(-)-Lactic acid is a normal intermediate in sugar fermentation (oxidation, metabolism). It is identified as a competitive inhibitor of ProDH (proline dehydrogenase) in plants.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms(R)-2-Hydroxypropionic acid
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite|ProDH
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number10326-41-7
-
Formula Weight90.08
-
Molecular FormulaC3H6O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 125 mg/mL (1387.66 mM)
-
SMILESC[C@@H](O)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
PAPA NONOate
PAPA NONOate is a pH-regulated NO donor.PAPA NONOate has potential antitumor activity and can be used to study diabetic wound healing disorders.
-
Guanosine 5'-triphos...
Guanosine 5'-triphosphate trisodium salt activates the signal transducing G proteins which are involved in various cellular processes including proliferation differentiation and activation of several intracellular kinase cascades.Proliferation and apoptosis are regulated in part by the hydrolysis of GTP by small GTPases Ras and Rho.
-
L-(-)-Malic acid
Malic acid is a tart-tasting organic dicarboxylic acid that plays a role in many sour or tart foods. Apples contain malic acid which contributes to the sourness of a green apple. Malic acid can make a wine taste tart although the amount decreases with increasing fruit ripeness.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


